Popular Science
2020-11-06
8002abstract
How to establish internal standards for low molecular weight siloxane D3~D10 testing and how to choose third-party outsourcing testing institutions? Let's explain one by one.
1、 Background
The presence of volatile low molecular weight siloxanes in silicone rubber can cause some problems during material use, but these problems can be solved by strictly controlling the content of low molecular weight siloxanes. To control the content of low molecular weight siloxanes, we first need to be able to test the content of low molecular weight siloxanes. The Guangmai technical team has conducted in-depth research on this issue and will share it with everyone below.
In the two testing standards for low molecular weight siloxanes D3~D10 introduced in the previous article, there are certain limitations on the scope of applicable materials, selection of standards, testing methods, etc.:
The standard ASTM F2466 is applicable to vulcanized silicone and requires direct quantitative calculation using D3~D10 as standard substances. In practical operation, it is not easy to purchase all kinds of pure cyclic siloxanes from D3~D10.
The standard GB/T 28112 is applicable to raw rubber, with D5 or D6 as the standard substance, and extrapolated by internal standard method.
In order to pursue more efficient, fast, and convenient testing methods, general institutions or enterprises will establish their own internal testing standards or seek help from third-party testing agencies.
2、 Establish internal testing standards
If you have GCMS equipment, you can establish your own internal testing standards. In order to simplify the testing process, the method of internal standard extrapolation is generally adopted.
The principle of internal standard extrapolation method: By using standard reference materials or GCMS qualitative analysis, the peak positions of various volatile methyl cyclic siloxanes can be determined. Due to the same proportion of carbon and hydrogen composition in methyl cyclic siloxane, the response values of each component of methyl cyclic siloxane with the same mass on the detector are consistent. Corresponding correction factors can be determined using standard and internal standards, and the residual amounts of each methyl cyclic siloxane can be extrapolated.
When using the internal standard extrapolation method to test the content of low molecular weight siloxanes, we must first establish a linear standard curve, and at the same time require the correlation coefficient of the established standard curve to meet 0.99 ≤ r ≤ 0.999. The detection limit of this method is the concentration of the standard solution diluted to three times the signal-to-noise ratio.
In addition to establishing standard curves, we also need to determine:
Sample pre-treatment: Selection of extraction methods, mainly including the selection of extractants, determination of extraction time, and clarification of the quality of extracted samples.
Selection of standard substances: Standard substances can be one or more, and increasing the types of standard substances can reduce the workload of establishing standard curves. However, standard solutions need to be prepared regularly, and the concentration of standard solutions needs to be strictly controlled.
Selection of internal standards: The selection of internal standards should follow the six principles defined, usually choosing normal tetradecane or normal hexadecane.
GCMS equipment parameter setting: including but not limited to carrier gas selection, determination of capillary column type, injection port temperature setting, design of heating and cooling curves, etc.
3、 Selection of Testing Institution
If there is no relevant testing equipment, in order to pursue faster testing speed and effective testing methods, we can seek help from third-party testing agencies.
It is worth noting that due to inconsistent testing methods and corresponding detection limits within each third-party testing agency, the final test results may have significant deviations. For example, we divided the sample in Figure 1 into three parts and directly sent them to three authoritative testing institutions A, B, and C for testing the total content of low molecular weight siloxanes D3-D10. The test results are shown in Figure 2.

Figure 1: Photos of samples to be sent for inspection to three testing institutions
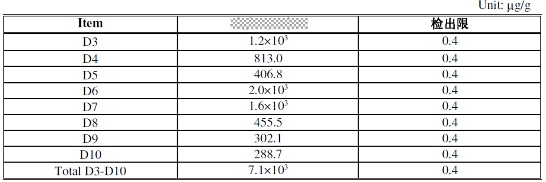

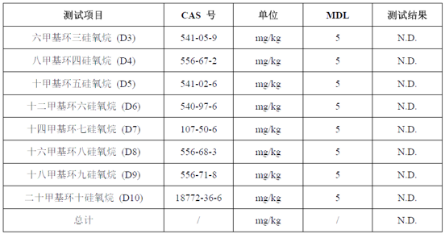
Figure 2 shows screenshots of test reports from authoritative testing institutions A, B, and C from top to bottom
It can be seen that the minimum detection limit of testing institution A is 0.4 ppm, and the total content of D3~D10 tested is 7100 ppm. The maximum detection limit of testing institution B is 30 ppm, and the total content of D3~D10 tested is 155 ppm. The detection limit of testing institution C is centered at 5 ppm, but none of D3~D10 were detected.
The above test results indicate that the deviation of the same sample in different testing institutions can be significant, and the test reports of different testing structures cannot be directly compared. Only reports from the same testing institution can be compared.
In order for our samples to pass the strictest customer testing, we need to choose more rigorous testing institutions as much as possible.
Conclusion
The testing of low molecular weight siloxanes D3~D10 is essential in electronic and optical equipment applications. Only the most rigorous testing can ensure the quality of our products and provide customers with a satisfactory answer.