Popular Science
2019-05-05
8428Summary:
The shortage of traditional energy and the increasingly prominent environmental problems have made the development of new energy vehicles, which can replace traditional cars, a hot topic of concern for people. The importance of safety issues in battery packs, as the core component of new energy vehicles, is evident. The internal temperature of the battery pack directly affects its safety, which in turn affects the overall safety of the vehicle. Improving the safety of battery packs requires controlling the internal structural temperature, therefore, increasing the overall heat dissipation performance of the structure is crucial. The use of liquid cooled plates has important application significance in ensuring the safety of battery packs and improving their service life.
key word:
Liquid cooled plate; Battery pack; dissipate heat; Cooling;
1、 Background introduction
As the main energy storage component in electric vehicles, battery modules are key components that directly affect the performance of electric vehicles. During the use of battery modules, due to the internal resistance of the cells, a certain amount of heat is generated during normal operation, causing the internal temperature of the module to rise. The normal operating temperature range of battery cells is 15-35 ℃. Exceeding 60 ℃ can pose certain safety hazards. The generation and rapid accumulation of heat will inevitably raise the internal temperature of the battery, especially when used in high-temperature environments or during high current charging and discharging, which may cause violent chemical reactions inside the battery and generate a large amount of heat. If the heat does not dissipate in time and rapidly accumulates inside the battery, the battery may experience leakage, deflation, smoking, and other phenomena. In severe cases, the battery may experience severe combustion or even explosion. To eliminate this danger, it is necessary to dissipate heat from the battery module to prevent the battery cells from being in a high-temperature state for a long time, which can affect their performance and reduce their service life.
2、 Classification of heat dissipation and cooling systems
At present, electric vehicles adopt cooling methods such as air cooling, liquid cooling, and heat pipes.
Heat pipe technology can meet the dual working conditions of high temperature heat dissipation and low temperature preheating for battery packs. It is sensitive to temperature changes and has good temperature uniformity. As a cooling system for battery packs, it has made certain progress. However, due to layout and volume limitations, there are various heat dissipation methods adopted in new energy power battery systems. Currently, the common application methods are air cooling and liquid cooling.
Air cooling is the use of a cooling fan to remove the heat absorbed by the radiator. It is relatively inexpensive and easy to install, but its heat dissipation performance is greatly affected by environmental and other factors, such as rising temperatures or overclocking. Compared with air cooling, liquid cooling is more expensive, but it has the advantages of quietness, stable cooling, and less dependence on the environment.
From the perspective of existing cooling methods for electric vehicle power batteries, air cooling has always occupied a major position, especially for Japanese electric vehicles, which basically use air cooling technology. With the increasing demand for batteries in application environments, liquid cooling has become a priority solution for automotive companies. China's mainstream electric passenger car companies have also begun to shift towards liquid cooling systems, and in the medium to long term, liquid cooling will dominate. The current application form is usually to install a liquid cooling plate in the battery module and inject liquid into the liquid cooling plate to dissipate heat from the battery cell. The actual working temperature of the liquid cooling plate is 10-20 ℃, and the circulating liquid refrigerant is used to remove heat and cool the battery to achieve the purpose of heat dissipation.
3、 Structure and working principle of liquid cooling plate
The battery module has certain requirements for the liquid cooled plate. Firstly, it has a high heat dissipation power, which can quickly dissipate the heat generated by the module and prevent a sharp rise in temperature; Secondly, it has high reliability. When vehicles are walking on the road, the battery pack in working condition must undergo various environmental tests, such as vibration, impact, high and low temperatures. The working voltage of the power battery pack is often several hundred volts, and the leakage of coolant will become a very serious problem. Even if a coolant with good insulation performance is used, its insulation performance will be immediately reduced when exposed to external substances, causing certain safety risks. Therefore, the sealing reliability of the liquid cooling plate is very important; Furthermore, the heat dissipation design should be precise to avoid excessive temperature differences within the system. The working temperature has a significant impact on the performance and aging of the battery; Finally, there is a requirement for weight. Currently, battery packs focus on lightweight, which requires every component inside the pack to be lightweight. If the liquid cooling plate takes up too much weight, it will directly affect the energy density of the battery module, which is unacceptable.
In response to the above issues, liquid cooled plates are generally designed with aluminum substrates embedded with copper tubes. This involves machining and milling grooves on the aluminum substrate using computer numerical control technology, and then pressing the bent copper tubes onto the aluminum substrate using a stamping machine, followed by brazing and welding. This design not only reduces the weight and cost of aluminum, but also fully utilizes the high thermal conductivity of copper pipes. Finally, two inlet and outlet ports are set up, and corresponding liquid refrigerants are injected, usually water or a mixture of water and organic alcohols (alcohols can prevent water from freezing at low temperatures). The water pump controls the circulation of the liquid. The reason for using water or its mixture with organic alcohols as a liquid cooling heat dissipation agent is that in physics, water has a much higher thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity than air, with a faster heat conduction rate and slower temperature rise. Therefore, water is an ideal heat dissipation medium. In battery packs, due to different environments, water is prone to freezing in low-temperature environments, which is very detrimental to heat dissipation. To solve this problem, a mixture of water and organic alcohols is generally used as the refrigerant, and the results have been well verified.
The working principle of a liquid cooling plate is that the excess heat generated by the battery is transferred through contact with the surface of the aluminum device. The liquid cooling system utilizes the high heat transfer coefficient of liquid flow to transfer high heat, which is ultimately carried away by the cooling liquid passing through the internal flow channels of the device.
The structure of a typical liquid cooled plate is shown in Figure 1:
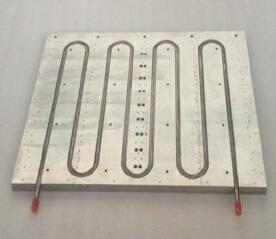
图1 电池包中液冷板结构
4、 Application of liquid cooled plate
In some typical applications of electric vehicles, liquid cooling plates can be divided into module level and cell level liquid cooling plates based on their cooling range.
The structure is shown in Figure 2:
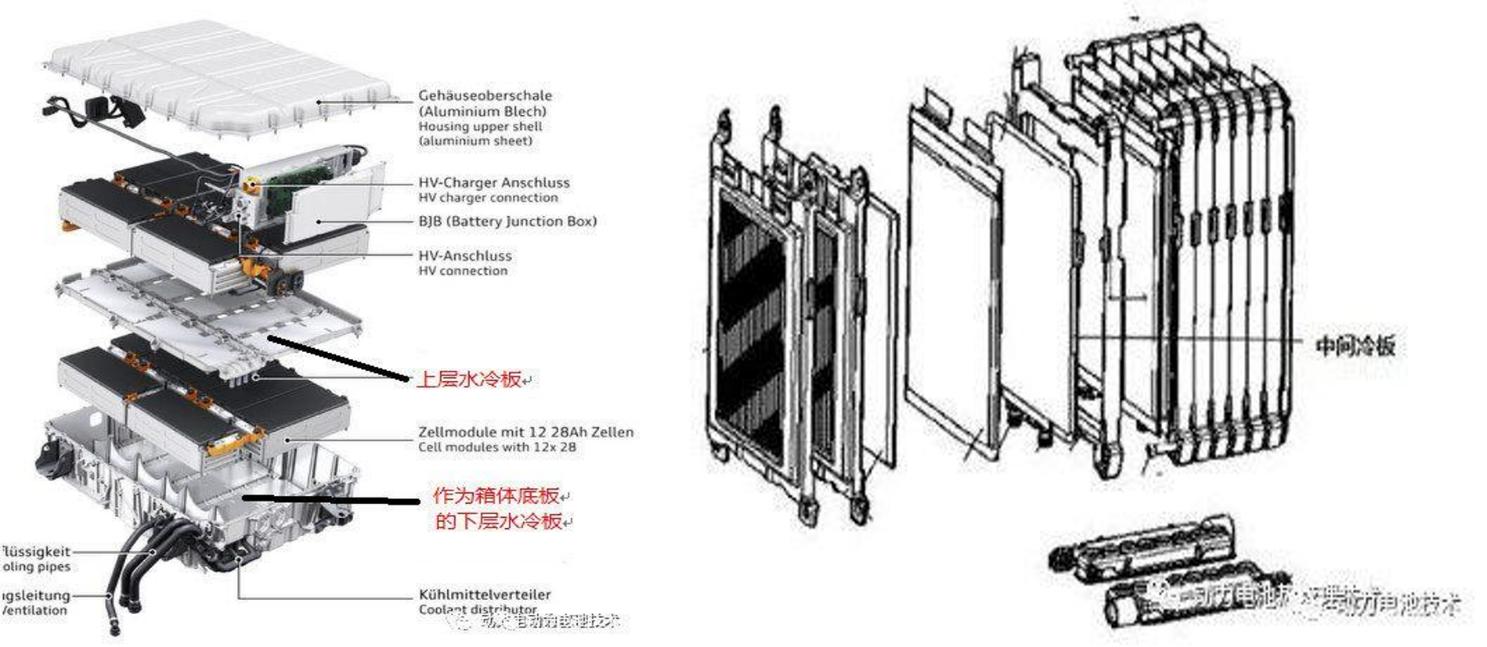
Figure 2: The positions of the module level liquid cooling plate (left) and the cell level liquid cooling plate (right)
The module level liquid cooling plate is a module inside the battery pack, usually placed under the battery module and in direct contact with the battery for heat dissipation. The design of each car manufacturer varies greatly, with most designs consisting of battery modules and liquid cooling plates, while a few manufacturers use a parallel structure of batteries and modules to better solve heat dissipation problems, from top to bottom consisting of battery modules, liquid cooling plates, battery modules, and liquid cooling plates (such as Audi Q7 PHEV).
The liquid cooled plate at the battery cell level is a part of the battery cell module that clamps the water-cooled plate between the battery cells, achieving better heat dissipation effect. Different types of designs may vary depending on the manufacturer.
According to the current application form, in battery packs, liquid cooling systems for square and cylindrical batteries are generally at the module level and are usually placed at the bottom of the battery box; Soft pack batteries have more battery cell levels.
5、 Problems and solutions encountered in the application of liquid cooled plates
During the use of the liquid cooling plate, some customers may encounter some problems: on the one hand, when testing the battery pack, they found that using breathable foam silicone as the shell seal, long-term use in a humid environment, the increase in humidity inside the battery pack and the temperature difference between the upper and lower surfaces of the liquid cooling plate can cause water vapor inside the battery pack to condense into liquid water below the liquid cooling plate, creating unsafe factors; On the other hand, the liquid cooling plate is in direct contact with the battery pack, which causes the liquid cooling plate to be in a load-bearing state for a long time. Coupled with its metal structure, it will undergo certain physical deformation, and the middle position will collapse to some extent. There will be gaps at the contact interface with the battery module, which is not conducive to heat transfer.
The current solution to the above two problems is to use glue or sealing rings to seal the battery pack shell, preventing the entry of external air; On the other hand, elastic materials such as springs or polypropylene foam (EPP) are used as supports between the bottom of the tray and the liquid cooling plate to prevent the sinking of the liquid cooling plate,
The overall design structure is shown in Figure 3:
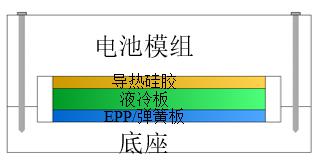
Figure 3: Design of Liquid Cooling Plate Support Structure
6、 Summary
At present, new energy vehicles have increasingly high requirements for power batteries, which are not only reflected in the system energy density and system power density, but also in various aspects of the battery pack. The increase in requirements also means that the total heat generation of the battery increases, which brings safety issues that cannot be ignored. Traditional air cooling technology can no longer meet the demand for highly integrated batteries, and liquid cooling solutions have gradually become mainstream. The effective heat dissipation of the liquid cooling plate provides a guarantee for the thermal management safety of the battery pack, allowing the heat of the battery to be effectively conducted. We believe that it will have broader application prospects and commercial value in new energy vehicles.
Original submission website: http://www.evpartner.com/news/4/detail-39782.html